Understanding Double Girder Bridge Cranes
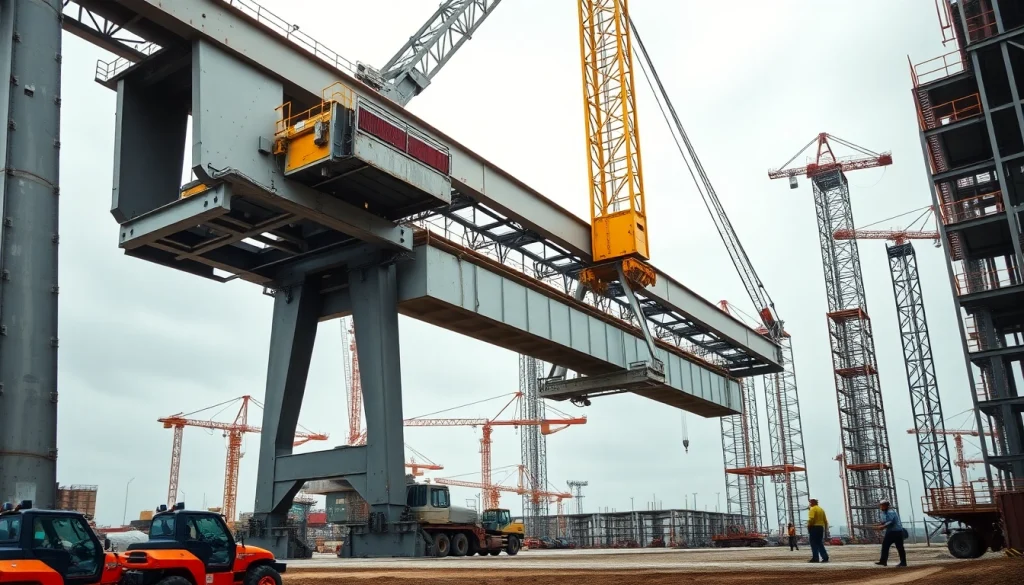
Double girder bridge cranes are essential tools in heavy lifting operations, offering stability and strength that meets the demanding requirements of various industries. These cranes utilize two parallel girders, which provide increased load capacity and wider spans compared to their single girder counterparts. When exploring options, a double girder bridge crane can be a viable choice for facilities needing efficient material handling solutions.
What is a Double Girder Bridge Crane?
A double girder bridge crane features two main girders that run parallel across the span of the facility. The hoisting mechanism typically travels on the lower flange of these girders, allowing for a more streamlined design that maximizes lifting height and capacity. The structure is supported at each end by trucks, which facilitate movement along overhead runways. This configuration distinguishes double girder cranes from single girder cranes, which comprise only one girder, impacting load stability and operational efficiency.
Advantages Over Single Girder Cranes
- Higher Load Capacities: Double girder cranes can lift heavier loads, often exceeding ten tons, making them ideal for demanding applications.
- Wider Span Capabilities: These cranes can span larger areas, accommodating expansive workspaces without sacrificing strength.
- Enhanced Stability: The dual girder design minimizes sway and enhances stability during operations, which is crucial for safety in heavy lifting.
- Improved Hook Height: The design allows for greater vertical lift, ensuring that loads can be lifted higher and dropped into place more efficiently.
Key Components and Their Functions
The key components of a double girder bridge crane include:
- Main Girders: The backbone of the crane, providing structural support and load-bearing capabilities.
- End Trucks: Located at each end of the girders, end trucks allow the crane to move along rails mounted on the building structure.
- Hoist Mechanism: Positioned between the girders, the hoist mechanism is responsible for lifting and lowering loads with precision.
- Trolley: This component moves along the girders, facilitating horizontal movement of the hoist and ensuring effective load handling.
Applications of Double Girder Bridge Cranes
Double girder bridge cranes are particularly versatile and are employed across various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and logistics. Their ability to handle heavy and bulky materials makes them a preferred choice in settings that demand robustness and reliability.
Industries Utilizing Double Girder Cranes
- Manufacturing: Used for moving heavy components and materials within production lines.
- Construction: Essential for lifting large materials, such as steel beams and concrete blocks on job sites.
- Shipbuilding: Vital for the construction and repair of ships where large components must be lifted and positioned accurately.
- Warehousing: Effective in warehouses for handling logistics operations, including loading and unloading transport vehicles.
Case Studies Illustrating Successful Implementations
Numerous successful implementations highlight the efficiency of double girder bridge cranes. For example, a major automotive manufacturer integrated double girder cranes into their assembly line, drastically reducing time spent on material transport and increasing overall productivity. This case demonstrates the crane’s ability to support heavy loads with minimal downtime.
When to Choose a Double Girder Over Other Cranes
Selecting a double girder crane is ideal when dealing with:
- Heavy load requirements (typically over ten tons)
- Long spans that exceed the capabilities of single girder cranes
- Operations requiring high lifting heights
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation and maintenance of double girder bridge cranes are critical to ensuring their safe and efficient operation. Following best practices can extend the lifespan of the crane and minimize operational disturbances.
Steps for Proper Installation of Double Girder Cranes
- Site Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the installation site, including structural integrity and space requirements.
- Mounting Rails: Install rails on which the end trucks will travel, ensuring they are level and securely fastened.
- Assemble Girders: Carefully assemble the main girders and connect them to the end trucks.
- Install Hoisting Mechanism: Position the hoist and trolley system on the girders before ensuring alignment and functionality.
- Testing: Perform functional testing to confirm that all systems operate correctly, including weight tests under safe conditions.
Regular Maintenance Checks and Protocols
Routine maintenance is essential to keep double girder cranes in optimal working condition. Typical maintenance procedures include:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly check for signs of wear, fraying cables, or structural damage.
- Lubrication: Keep moving parts lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
- Load Testing: Periodically perform load tests to ensure the crane can handle its specified capacity safely.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues with double girder cranes include:
- Electrical Failures: Check connections and power supply.
- Mechanical Issues: Inspect for misalignments or wear on moving parts.
- Operational Problems: Ensure the operator is trained and familiar with the crane’s controls.
Safety Considerations and Compliance
Safety must be a priority when operating double girder bridge cranes, as improper use can lead to accidents and injuries. Understanding compliance with safety regulations is crucial for operators and organizations alike.
Understanding OSHA Regulations and Standards
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) outlines several regulations governing the use of cranes in the workplace. Familiarity with these standards helps organizations remain compliant and ensure safety:
- Regular safety audits and inspections
- Proper operator certification and training
- Use of safety devices such as limit switches and emergency stops
Best Safety Practices for Operators
Implementing best practices can enhance safety during crane operations:
- Pre-Operation Checks: Always perform checks before operating the crane to identify potential issues.
- Clear Communication: Use hand signals or radios for effective communication between operators and ground personnel.
- Load Management: Ensure loads are within the crane’s capacity and properly secured before lifting.
Training Programs for Crane Operators
A robust training program is essential for operators to ensure safe and efficient use of double girder bridge cranes. Programs should cover:
- Understanding the crane’s mechanical and electrical systems
- Operational procedures, including emergency protocols
- Best safety practices for handling loads and maintaining equipment
Future Trends in Crane Technology for 2025
The crane industry is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and increasing efficiency demands. As we approach 2025, several trends are anticipated to reshape the landscape of double girder bridge cranes.
Innovations in Double Girder Bridge Crane Designs
Future designs are likely to focus on improved materials and lighter weight construction, enhancing the cranes’ ability to lift heavier loads while maintaining efficiency. Innovations such as modular designs may allow for easier transport and installation.
The Role of Automation and IoT in Crane Operations
As the Internet of Things (IoT) becomes more prevalent, expect to see cranes integrated with smart technology for real-time monitoring. This can include load sensors, operating condition monitoring, and predictive maintenance alerts that enhance operational efficiency.
Predictions for Industry Growth and Developments
With the ongoing demands for higher efficiency and safety in material handling, the double girder bridge crane market is expected to see significant growth. As industries become more reliant on automation and advanced technology, the future will bring innovations that not only enhance performance but also emphasize sustainability and compliance with environmental standards.